Climate... As Agriculture is reeling in Yemen
2024-08-09
Bassam Al-Qadhi - (hjf)
"This year's harvest season came to a close with barren fields, leaving us with nothing to gather, not even a single kilogram of white corn," laments Qubla Ahmed, the rural farmer from the Sanah region in Al-Dhale Governorate, southern Yemen.
She further elaborates, "We solely rely on agriculture, our lifeline for decades. However, the seasons have changed, rainfall has decreased, and the soil no longer yields as abundantly as before." She grimly notes their struggle to stave off hunger for their children, surviving on relief assistance, or else "we will die of hunger."
Earlier, the three United Nations agencies, namely the World Food Programme (WFP), UNICEF, and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), stated that Yemen is one of the countries suffering from the most severe food insecurity globally.

According to the FAO, more than two-thirds of Yemen's population is at risk of hunger, making them urgently in need of aid "to save their lives and maintain their livelihoods."
The FAO, states that climate change directly and indirectly impacts agricultural output because of changes in rainfall patterns, droughts, floods, and the geographical spread of pests and diseases. This presents a challenge in eradicating hunger, as it is a fundamental aspect of sustainable development that cannot be tackled without addressing climate change.
According to The World Bank, Yemen is considered one of the countries most affected by climate change globally.

A Severe Impact
According to a study by Dr. Ali Ahmed Daif Allah, a geography professor at Thamar University, Yemen faces various environmental challenges, with one of the most significant being climate change. This will have a harsh impact on the region, given its dry climate and scarce water resources. Dr. Ali expects "an increase in drought conditions and evaporation rates - already high - in the area, making it one of the most vulnerable regions to the effects of climate change. This will lead to more frequent drought waves, resulting in decreased agricultural productivity and a lack of food and water security."
The study published in the "Ruoaa' Magazine for Literature and Humanities" in September 2020 recommended that the relevant government entities in Yemen should strive with all available resources and mechanisms to secure the necessary funding to implement measures to adapt to the effects of climate change in Yemen.
The fifty-year-old farmer, Mohammed Thabet Abdullah, who resides in Radfan countryside in Lahij Governorate, southern Yemen, recalls, "A decade ago, agriculture on our land used to cover about 80% of our family's food." Unfortunately, today we no longer cover more than 20%. Agriculture is no longer our main source of income."
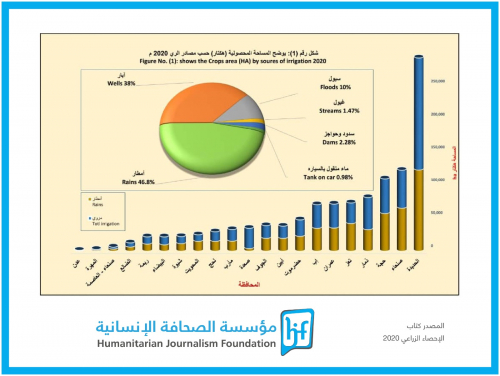
In addition to climate change, drought, rising temperatures, delayed rainfall, and changing weather patterns, Thabet points to "water resource scarcity, prolonged war, and government neglect in supporting farmers."
Decline in Agricultural Production
"The deterioration of the agricultural sector is a catastrophe threatening millions of people with famine, malnutrition, food insecurity, and loss of livelihoods. Will the government and country's leadership take action against the deterioration Yemen is experiencing?" laments Thabit Abdullah bitterly.
In this regard, a study conducted by Tamdeen Foundation in partnership with Oxfam on "Climate Change and its Impact on Food Security and Livelihoods in Al-Ma'afir and Al-Shamaitain Directorates in Ta'izz Governorate," in the centre of Yemen, revealed that 89% of farmers experienced a change in their primary source of income over the past twenty years. Rainfall in the region has decreased, and its seasons have shifted, accompanied by temperature fluctuations and an increase in drought conditions, leading to 73% of farmers suffering from food insecurity.

The study, published in early February 2023, emphasized the importance of addressing the issue of climate change and integrating it as a top priority within the current national development agenda. Urgent measures and actions must be taken to mitigate the challenges posed by climate change as failure in this issue could lead to more frequent climate disasters in Yemen, amidst water and food insecurity and land degradation. As a result, local and international crisis response efforts in Yemen will not be effective unless there is an enhanced capacity to adapt to climate change.
Yemen and Climate Change
Engineer Tawfiq Al-Sharjabi, the minister of Water and Environment, in the internationally recognized government, , affirms that climate change affects all vital sectors, with water and agriculture being at the forefront.
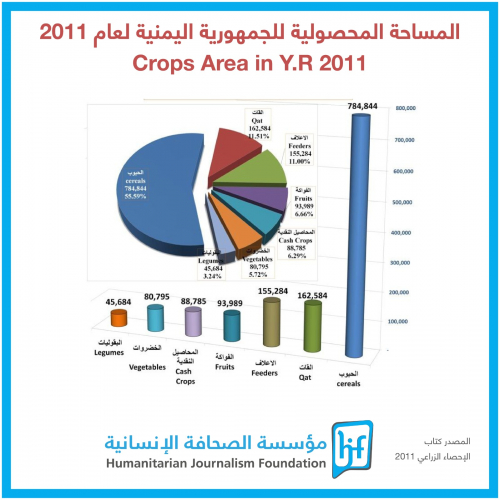
"Its impacts on the agricultural sector, which is the backbone of Yemen, are manifested in drought, desertification, sand encroachment, and the decreased resilience of some crops to climate change, leading to a decline in agricultural production levels, which is a major threat to food security," Al-Sharjabi adds.
Discussing the repercussions of "climate change on the water sector, and thus on irrigating agricultural crops, potentially diminishing agricultural output in numerous regions," he highlighted how these effects extend to coastal zones, particularly tropical storms along the eastern shores impacting fishing industries, alongside rising sea levels and temperature fluctuations in certain areas.
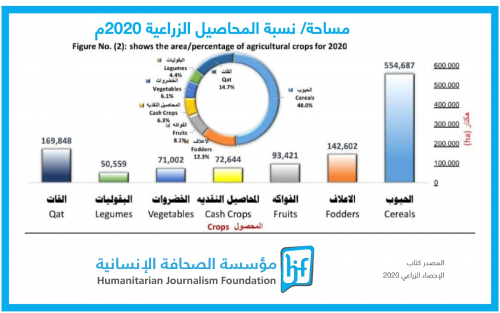
The minister admitted the lack of a comprehensive national strategy to tackle the repercussions of climate risks on food security. He mentioned that "a proposal for an adaptation plan will be submitted for funding from the Green Climate Fund, alongside a dedicated strategy for food security, water resources, and agriculture."
Shargabi highlights the crucial role of internationally recognized organizations affiliated with climate funds in partnering with relevant entities to secure climate financing. This funding is poised to aid Yemen in mitigating numerous effects of climate change, specifically its impact on food security.

The Severity of The Climate Phenomenon
Majed Najmi, the Director of the Food Security Department at "Yemen Aid" organization, describes climate change as a natural occurrence influenced by human activities. It is anticipated to negatively affect various aspects of life in Yemen, particularly the agricultural and livestock sectors, placing a burden on farmers who will face environmental, economic, and social consequences as a result.
Najmi emphasized the necessity of adapting to this phenomenon to protect the livelihoods of agricultural workers and maintain local food security. To ensure the success of adaptation efforts, farmers must understand the nature, dimensions, and various impacts of this phenomenon.

He added: changes in temperature and rainfall patterns negatively affect crop yields, leading to a decrease in food availability. Typically, a decline in crops results in higher food prices and reduced agricultural livelihood incomes, both of which reduce opportunities for affected families to access food. Consequently, there is a lack of feed and food for livestock and animals.
Water is The Primary Obstacle
Furthermore, a study revealed that water scarcity poses a significant obstacle to the development and increased agricultural production rates. Yemen has been affected by heat and water scarcity, along with rising temperatures leading to a 75% decrease in water flow. There is also a possibility of an increase in Yemeni land aridity by 50% to 60%.
The study published in the Journal of Agricultural Sciences on December 31, 2020, emphasized the necessity of giving adequate attention to the food production sector to keep pace with population growth in Yemen and meet the population's food needs.

The lead researcher of the study, Dr. Adnan
Al-Sanawi, Professor of Agricultura Economics at Sanaa University, emphasized that 80% of Yemen's agricultural sector relies on rainfall. He pointed out that Yemen is facing its biggest challenges in recent history, including the ongoing conflict and climate change.
Moreover, approximately 97% of grain imports are relied upon in Yemen, accounting for 90% of wheat products and constituting between 35% and 46% of the daily calorie intake per person, as indicated by the Economic and Social Updates Bulletin in Yemen, Issue 74 from July 2022. Yemen stands as one of the nations heavily impacted by the consequences of climate change on a global scale, primarily due to its fundamental reliance on imported food supplies.
The scarcity of water remains the primary obstacle to improving agricultural productivity. While floods have eroded soil and led to the loss of agricultural land, resulting in a decrease in agricultural land from 1.6 million hectares in 2010 to 1.2 million hectares in 2020, the depletion of water resources will lead to a 40% decline in agricultural productivity.
Yemen is considered one of the countriessuffering most from water scarcity globally, ranking seventh in this regard. Approximately 18 million citizens struggle to access safe water, and the country faces water stress, ranking 20th among the world's countries most vulnerable to this stress, according to the World Resources Institute.
Global Climate Impact

Estimates indicate that the global impact of climate change poses another threat to food security in Yemen, which imports 90% of its needs. This will exacerbate food insecurity, nutritional deficiencies, and reliance on external aid.
The drought conditions have occurred alongside an unparalleled increase in temperatures in recent years, affecting every agricultural region in the nation. As per official reports, the desertification rate has risen from 90% in 2014 to 97% in 2022, resulting in an annual loss of arable land ranging from 3 to 5%.
Proposed Solutions
Majed Najmi, the Food Security Department Manager at Yemen Aid Organization, emphasizes the importance of supporting farmers with modern technologies that use concentrated feed and salt blocks to preserve the livestock sector. Additionally, supporting them in establishing protected houses for agricultural crops and providing seedlings and seeds.
He also emphasized that one of the most important proposed solutions for adapting to the effects of climate risks is to support irrigation sources with clean energy instead of diesel generators and pumps to save money and preserve the environment. Additionally, supporting greening of streets and cities, which in turn will help address climate change.

Government Measures
In response to the proposed solutions and remedies to mitigate the exacerbation of climate change impacts, the Minister of Water and Environment emphasizes that the government's primary role should currently focus on integrating climate change issues into economic recovery and development agendas. Climate change topics, whether related to adaptation or clean development, should be among the priorities for economic recovery. Additionally, there should be updates to sectoral plans and strategies to incorporate climate change issues within them.
Al-Sharjabi added, "There are numerous measures to adapt to climate change, including interventions and projects needed by affected sectors such as water, agriculture, coastal areas, and others. However, the most important adaptation measure lies in establishing the necessary institutional arrangements, which are summarized in preparing the National Adaptation Plan."
One of the adaptation measures to address the impacts of climate risks, as mentioned by the Minister of Water and Environment, is identifying and evaluating priority interventions across all sectors. This includes establishing databases and climate-related information through rehabilitating climate monitoring networks and constructing new stations, as well as implementing projects and interventions based on comprehensive climate vulnerability assessments.
The impact of climate is evident.
Climate change and its effects are clearly evident in Yemen, as highlighted by Engineer Mohammed Al-Nashili, the General Director of the General Administration for Agricultural Marketing and Trade at the Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation, and Fish Wealth: Droughts, severe floods, pests, disease outbreaks, changes in rainfall patterns, increased frequency and intensity of storms, and rising sea levels pose a threat to natural systems in the country and communities that rely on natural resources.

"The agriculture sector is in dire need of revitalization, as its annual GPD has barely reached 2.3% on average, falling short of the targeted growth rate of 1.6% set in previous plans. This stagnation is attributed to climate changes that have significantly impacted local production and the country's food security status. Among these impacts are the damages caused by storms, hurricanes, and floods that ravaged Yemeni regions during the period of 2010 - 2023," Al-Nashili remarked.
He further adds, "The damages also include rainfall shortages, off-season rains, droughts, and desertification. Agricultural lands have suffered significant harm due to increased soil salinity and the erosion of vast areas, leading to a decrease in cultivated land area, a shortage of fruit trees, and the loss of livestock and bee colonies, affecting the livelihoods of the population."

The government official explained that grain crops, including maize at 60%, sorghum at 15%, and wheat at 13%, occupy the largest area in the country. However, production has decreased due to rainfall shortages, climate change, rising temperatures, fluctuating rainfall amounts, a shortage of improved varieties adapted to rainy conditions, and diseases affecting fruits and vegetables.
The most affected agricultural crops are date palms and citrus trees, as floods and hurricanes destroyed thousands of date palm trees, reducing date production by 60%. This also caused extensive damage to vegetables, especially in high-altitude and mid-altitude regions.
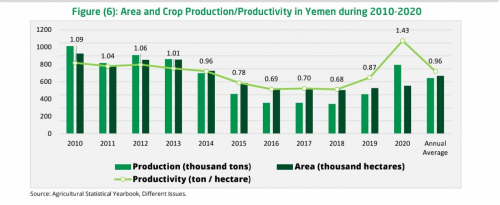
Government Efforts
"The Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation, and Fish Wealth is exerting efforts to mitigate the severity of climate change, but they are not sufficient. There is a need to enhance resilience and adaptation through collaboration between governmental, non-governmental, and international efforts," Al-Nashili added.
One of the ministry's most important efforts, according to the Director-General of Agricultural Marketing and Trade, is "participation in international forums, including COP28, ، and considering climate change a priority for the ministry. This includes preventing urban sprawl at the expense of agricultural land, developing legislation related to climate change, updating climate data and early warning systems, and preparing a food security plan to reduce the impact of climate change."
The Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture
In the same context, Nawaf Abkar, an agricultural engineer specializing in irrigation systems, emphasizes that climate change can have a negative impact on agriculture in Yemen. It can lead to soil degradation and a decline in crop quality, ultimately affecting agricultural production and hindering food security.

Abkar, who also serves as the Executive Director of the Green Development and Environmental Foundation in the capital Aden, explained that the most affected agricultural crops in Yemen due to climate change are wheat, barley, coffee trees, and potato crops, which are essential crops for the country.
He expressed that adopting resilient varieties can pave the way to weather climate changes and tackle their repercussions on the agricultural sector. Enhancing plant cultivation to develop agricultural varieties that can withstand climate changes, promoting the use of efficient irrigation techniques to improve water consumption sustainability, adopting sustainable agricultural practices for rural infrastructure development, along with encouraging farmers to adopt sustainable agricultural practices to enhance adaptation to climate change impacts.
"We expect the Yemeni government to adopt policies that encourage the modernization of agricultural technology, provide financial support and training for farmers to implement sustainable practices, and invest in enhancing rural infrastructure for effective integration in adapting to climate change impacts," Abkar emphasizes.
Food Insecurity

With three out of every four Yemenis relying on agriculture and livestock for their survival, the climate crisis is pushing communities already suffering from prolonged conflict to the brink of collapse, according to the International Committee of the Red Cross
Approximately 17 million people, or around 60% of the population, are grappling with hunger, chronic food insecurity, and malnutrition, according to the World Bank report. These challenges are among the most pressing in Yemen, amplified by significant exposure to devastating climate change impacts and the enduring conflict in the region.
The climate change vulnerability index "INFORM" for Yemen in 2022 reached a score of 8.1, ranking third globally among the countries most susceptible to climate change and least prepared to face its shocks.
Yemen, grappling with a humanitarian crisis, ranks as the worst globally, holding the 171st position out of 182 countries on the Notre Dame Global Adaptation Index, which assesses vulnerability to climate change and readiness to adapt to it.

General Supervision: Nashwan Al-Othmani
Design and infographic: Hussein Al-Anami
Bassam Al-Qadhi is a scientific covering climate, environmental, and health issues.
Translated by: Amira Yehia
This investigation was produced with the support and supervision of the Humanitarian Journalism Foundation (HJF) as part of the #Yemen_Climate_Emergency campaign.




